Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that your body can’t make on its own, so you need to get it from your diet or from supplements.
Vegetarians, people who are pregnant or nursing, and others who are at risk of deficiency may want to track their diets closely to make sure they’re getting enough.
Here are foods rich in vitamin B12 to add to your shopping list.
Good sources of vitamin B12
1. Animal liver and kidneys
Organ meats are some of the most nutrient-packed foods. Liver and kidneys, especially from lamb, are rich in vitamin B12.
A 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of lamb liver provides an incredible 3,571% of the Daily Value (DV) for vitamin B12.
While lamb liver is generally higher in vitamin B12 than beef or veal liver, the latter two may still contain about 3,000% of the DV per 3.5 ounces (100 grams).
Lamb’s liver is also very high in copper, selenium, and vitamins A and B2.
Lamb, veal, and beef kidneys are likewise high in vitamin B12. Lamb’s kidneys provide about 3,000% of the DV per 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving, plus more than 100% of the DV for vitamin B2 and selenium.
2. Clams
Clams are small, chewy shellfish that are packed with nutrients.
This mollusk is a lean source of protein and contains very high concentrations of vitamin B12. You can get more than 7,000% of the DV in just 20 small clams (190 grams).
Clams, especially whole baby clams, also provide a great amount of iron, with almost 200% of the DV in a 100-gram (3.5-ounce) serving.
Plus, clams have been shown to be a good source of antioxidants.
Interestingly, the broth of boiled clams is also high in vitamin B12. Canned clam broth has been shown to provide 113–588% of the DV per 3.5 ounces (100 grams).
3. Sardines
Sardines are small, soft-boned saltwater fish. They’re usually sold canned in water, oil, or sauces, though you can also buy them fresh. Sardines are especially nutritious because they contain good amounts of almost every single nutrient.
A 1-cup (150-gram) serving of drained sardines provides 554% of the DV for vitamin B12.
Furthermore, sardines are an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to provide many health benefits, such as reducing inflammation and improving heart health.
4. Beef
Beef is an excellent source of vitamin B12.
One grilled flat iron steak (about 190 grams) provides 467% of the DV for vitamin B12.
Also, the same amount of steak contains reasonable amounts of vitamins B2, B3, and B6, as well as more than 100% of the DVs for selenium and zinc.
If you’re looking for higher concentrations of vitamin B12, it’s recommended to choose low-fat cuts of meat. It’s also better to grill or roast it — instead of frying — to preserve the B12 content.
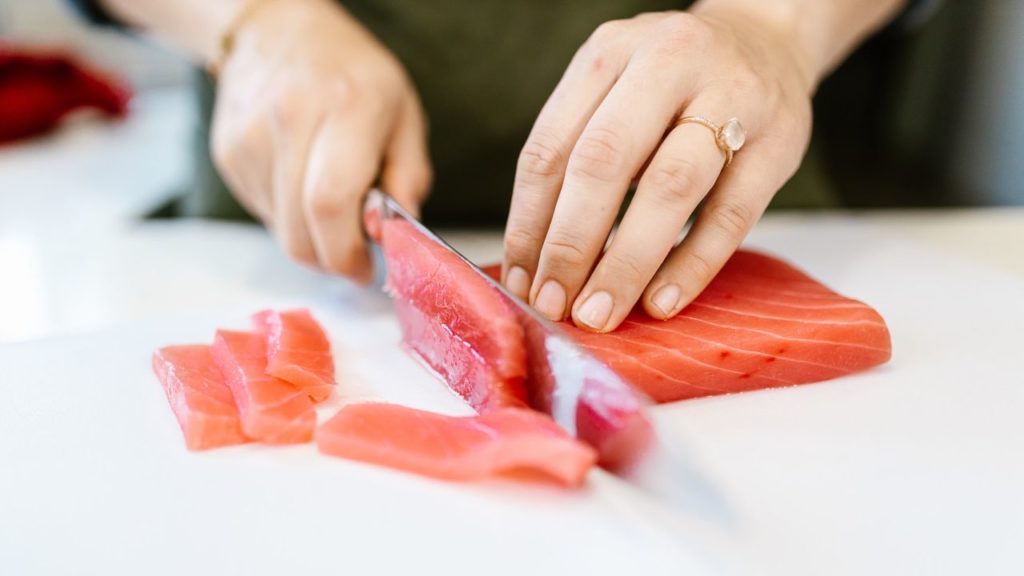
5. Tuna
Tuna is a commonly consumed fish and a great source of nutrients, including protein, vitamins, and minerals. It contains high concentrations of vitamin B12, especially in the muscles right beneath the skin, which are known as dark muscles.
A 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of cooked tuna contains 453% of the DV for the vitamin.
This same serving size also packs a good amount of lean protein, phosphorus, selenium, and vitamins A and B3.
Canned tuna also contains a decent amount of vitamin B12. In fact, a can (142 grams) of light tuna canned in water contains 152% of the DV.
6. Trout
Rainbow trout is considered one of the healthiest fish. This freshwater species is a great source of protein, healthy fats, and B vitamins.
A 3.5-ounce (100-gram) serving of trout fillet offers about 312% of the DV for vitamin B12 and 1,171 mg of omega-3 fatty acids.
For adults, experts recommend a combined daily intake of 1,100–1,600 mg of omega-3 fatty acids.
Trout is also a great source of minerals such as manganese, phosphorus, and selenium.
7. Salmon
Salmon is well known for having one of the highest concentrations of omega-3 fatty acids. It’s also an excellent source of B vitamins.
A half fillet (178 grams) of cooked salmon can pack 208% of the DV for vitamin B12.
The same serving may also provide 4,123 mg of omega-3 fatty acids.
Alongside its high-fat content, this fish offers a high amount of protein, with about 40 grams in a half fillet (178 grams).
8. Milk and dairy products
Milk and other dairy products, such as yogurt and cheese, are great sources of protein and several vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B12.
One cup (240 ml) of whole milk supplies 46% of the DV for vitamin B12.
Cheese is also a rich source of vitamin B12. One large slice (22 grams) of Swiss cheese contains about 28% of the DV.
Full-fat plain yogurt may also be a decent source. It has even been shown to help improve vitamin B12 status in people who are deficient in this vitamin.
Interestingly, studies have found that your body absorbs the vitamin B12 in milk and dairy products better than the vitamin B12 in beef, fish, or eggs.
9. Eggs
Eggs are a great source of complete protein and B vitamins, especially B2 and B12.
Two large eggs (100 grams) supply about 46% of the DV for vitamin B12, plus 39% of the DV for vitamin B2.
Research has shown that egg yolks have higher levels of vitamin B12 than egg whites. The B12 in egg yolks is also easier to absorb. Therefore, it’s recommended to eat whole eggs instead of just their whites.
In addition to getting a good dose of vitamin B12, you’ll get a healthy amount of vitamin D. Eggs are one of the few foods that naturally contain it, with 11% of the DV in two large eggs.
Should you use supplemental vitamin B12?
Those at risk of vitamin B12 deficiency, including older people, those who are pregnant or breastfeeding, vegetarians and vegans, those with digestive issues, and those who have had stomach surgery, are advised to take vitamin B12 supplements.
B12 in supplements, like B12 in fortified foods, is synthetic and therefore vegan-friendly .
Vitamin B12 supplements are available in numerous forms. They can be swallowed, chewed, ingested, or placed under the tongue. A medical professional can also administer vitamin B12 injections.
Vitamin B12 administered orally and intramuscularly are equally effective at restoring B12 levels in deficient individuals, according to research.
In fact, one study indicated that individuals with low vitamin B12 levels repleted their stockpiles after 90 days of supplementation or injections.
The conclusion
Vitamin B12 is a crucial nutrient required by the body for numerous critical processes.
It is abundant in animal products, fortified foods, and nutritional supplements. Liver, steak, sardines, clams, and dairy products are some of the richest sources.
Eating these foods may significantly benefit your overall health, whether your goal is to build your vitamin stores or prevent deficiency.